Speech Therapy

What is Speech Therapy?
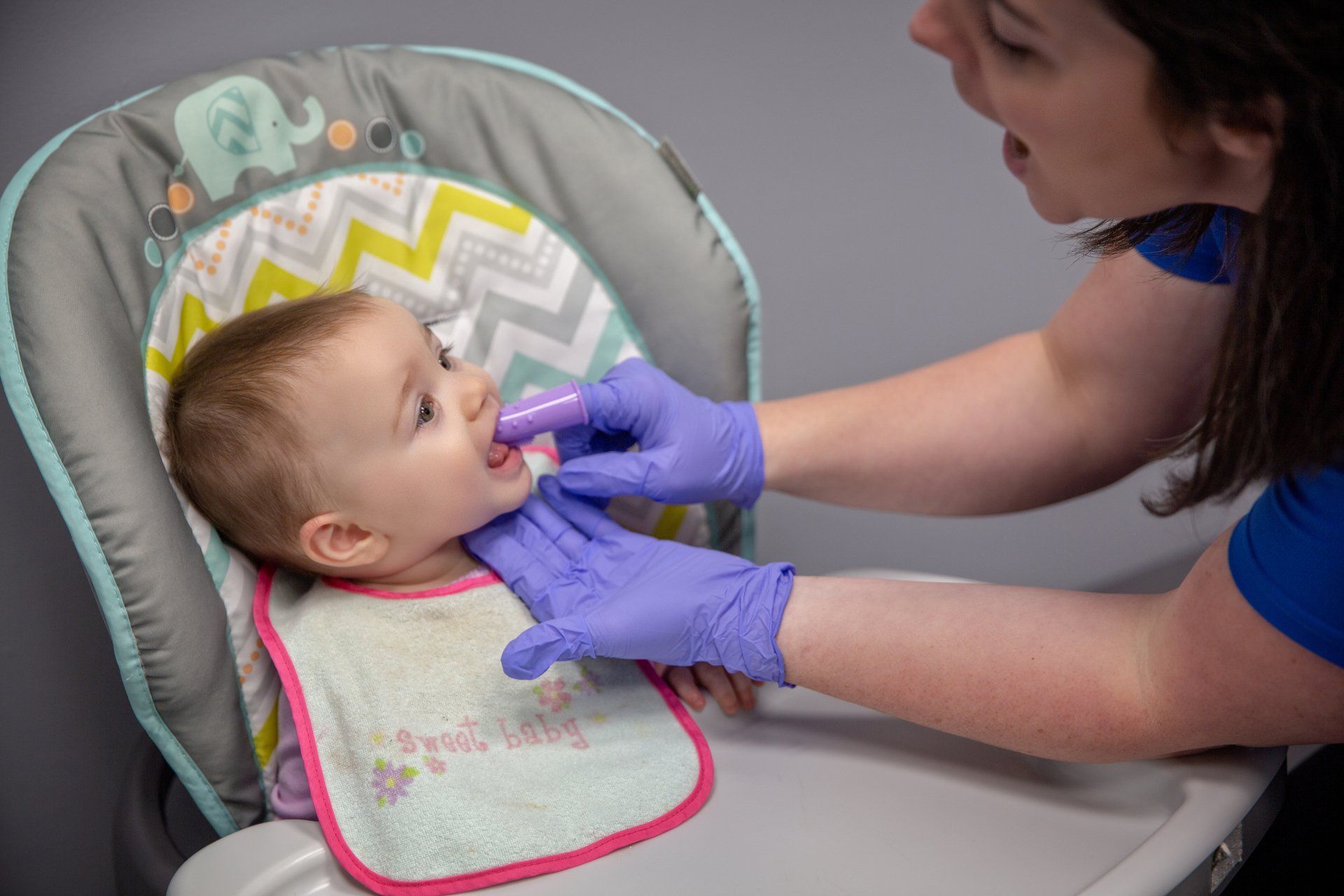
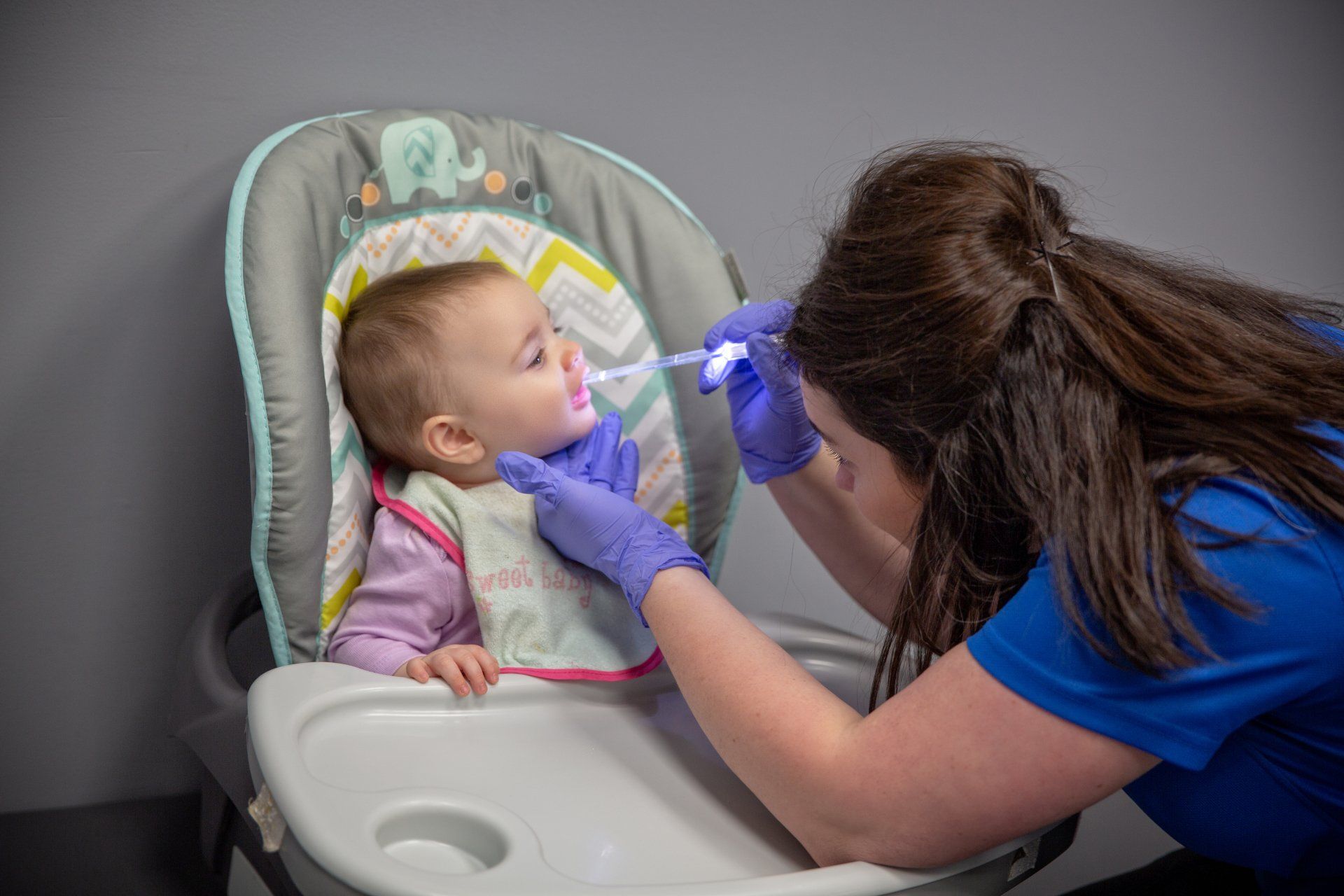
Speech therapy involves a Speech-Language Pathologist’s (SLP) assessment of speech, language, cognitive-communication, and oral/feeding/swallowing skills to identify types of communication problems (articulation; fluency; voice; receptive and expressive language disorders, etc.) and the best way to treat them.
Speech Therapy for Kids
Kids might need speech-language therapy for a variety of reasons, including, but not limited to:
- hearing impairments
- cognitive (intellectual, thinking) or other developmental delays
- weak oral muscles
- chronic hoarseness
- birth defects such as cleft lip or cleft palate
- autism
- motor planning problems
- articulation problems
- fluency disorders
- respiratory problems (breathing disorders)
- feeding and swallowing disorders
- traumatic brain injury
Pediatric and School-based Services:
(Treatment is needed for one or more of the following disorders.)
- Articulation disorders: difficulties producing sounds in syllables or saying words incorrectly to the point that listeners can’t understand what’s being said.
- Fluency disorders: problems such as stuttering, in which the flow of speech is interrupted by abnormal stoppages, partial-word repetitions (“b-b-boy”), or prolonging sounds and syllables (sssssnake).
- Resonance or voice disorders: problems with the pitch, volume, or quality of the voice that distract listeners from what’s being said. These types of disorders may also cause pain or discomfort for a child when speaking.
- Receptive language disorders: difficulties understanding or processing language.
- Expressive language disorders: difficulty putting words together, limited vocabulary, or inability to use language in a socially appropriate way.
- Cognitive-communication disorders: difficulty with communication skills that involve memory, attention, perception, organization, regulation, and problem solving.
- Dysphagia/oral feeding disorders: disorders in the way someone eats or drinks, including problems with chewing, swallowing, coughing, gagging, and refusing foods.
Speech Therapy for Adults
Adults may experience speech and language difficulties for a variety of reasons. Conditions that may cause them is include:
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Dementia
- Huntington’s Disease
- Laryngeal Cancer
- Oral Cancer
- Right Hemisphere Brain Injury
- Stroke
- Traumatic Brain Injury
Adult and Geriatric Services:
- Speech treatment to improve oral motor muscle strength, coordination, and speed
- Language treatment to improve receptive and expressive communication following neurological impairments
- Dysphagia treatment to improve swallowing sequence and coordination to safely consume a regular diet
- Voice treatment to improve breath support for speech production, pitch, volume, and overall quality of voice
- Communication treatment to improve individuals’ ability to communicate verbally and non-verbally through communication aids/devicesNew Paragraph